According to cybersecurity researchers, threat actors attempting to obtain unauthorized access to sensitive data may use third-party plugins for OpenAI ChatGPT as a new avenue of attack.
New study from Salt Labs suggests that security holes in ChatGPT and its ecosystem could let attackers install malicious plugins without users’ permission and take over accounts on unaffiliated websites like GitHub.
You might also be interested: There Are Over 225,000 Stolen ChatGPT Credentials For Sale On The Dark Web.
As the name suggests, ChatGPT plugins are programs created to operate on top of the large language model (LLM) in order to retrieve current data, do calculations, or access external services.
Since then, OpenAI has also released GPTs, customized variants of ChatGPT designed to meet certain use cases and lessen reliance on outside services. Users of ChatGPT will no longer be able to install new plugins or start new discussions with already-existing plugins as of March 19, 2024.
One of the vulnerabilities that Salt Labs found entails using the OAuth procedure to deceive a user into installing a random plugin by taking advantage of ChatGPT’s failure to verify that the user actually initiated the plugin installation.
Threat actors may be able to use this to effectively intercept and steal all of the victim’s shared data, including potentially confidential information.
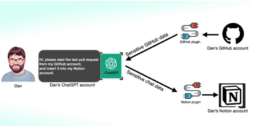
The cybersecurity company also discovered PluginLab vulnerabilities that may be used as a weapon by hostile actors to launch zero-click account takeover assaults, giving them access to an organization’s source code repositories and control over its account on unaffiliated third-party services like GitHub.
“[The endpoint] ‘auth.pluginlab[.]ai/oauth/authorized’ does not authenticate the request, which means that the attacker can insert another memberId (aka the victim) and get a code that represents the victim,” Aviad Carmel, a security researcher, noted. “With that code, he can use ChatGPT and access the GitHub of the victim.”
To retrieve the victim’s memberId, send a query to the API “auth.pluginlab[.]ai/members/requestMagicEmailCode.” There is no proof that the vulnerability has been used to breach any user data.
An OAuth redirection manipulation flaw was also found in a number of plugins, including Kesem AI. This bug might allow an attacker to send a carefully designed link to the victim, thereby obtaining the account credentials linked to the plugin itself.
The news was released a few weeks after Imperva revealed two ChatGPT cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities that could be used to take over any account.
Johann Rehberger, a security researcher, also showed in December 2023 how malevolent actors could construct Custom GPTs that could phish for user credentials and send the stolen information to a remote server.
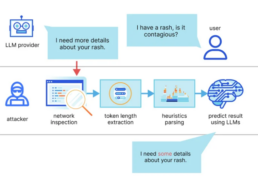
A Novel Attack on AI Assistants via Remote Keylogging
The results also come in the wake of fresh research this week regarding an LLM side-channel attack that uses token-length as a stealthy way to get encrypted responses from AI Assistants via the internet.
According to researchers from Ben-Gurion University and the Offensive AI Research Lab, “LLMs generate and send responses as a series of tokens (akin to words), with each token transmitted from the server to the user as it is generated.”
“Even though this operation is encrypted, a new side-channel known as the token-length side-channel is revealed by the sequential token transfer. Even with encryption, the length of the tokens can be deduced from the size of the packets, which could lead to network attackers deducing private and sensitive information exchanged in these kinds of interactions.”
This is achieved through the use of a token inference attack, which trains an LLM model to translate token-length sequences into their plaintext equivalents in normal language, thereby deciphering responses in encrypted communication.
Stated differently, the fundamental concept involves utilizing an LLM provider to intercept real-time chat responses, deduce token lengths from network packet headers, extract and parse text segments, and utilize a customized LLM to determine the response.
An AI chat client in streaming mode and an adversary with the ability to record network data between the client and the AI chatbot are two essential requirements for executing the assault.
It is advised that businesses creating AI assistants use random padding to mask the true length of tokens, send tokens in larger groups rather than one at a time, and send entire responses all at once rather than one token at a time to mitigate the side-channel attack’s effectiveness.
“Balancing security with usability and performance presents a complex challenge that requires careful consideration,” the study’s authors stated.
MANAGED CYBERSECURITY SOLUTIONS
Rhyno delivers a range of activities that combine to fully protect your infrastructure and data from cybercriminals, anywhere and everywhere, 24/7/365.
About Rhyno Cybersecurity Services
Rhyno Cybersecurity is a Canadian-based company focusing on 24/7 Managed Detection and Response, Penetration Testing, Enterprise Cloud, and Cybersecurity Solutions for small and midsize businesses.
Our products and services are robust, innovative, and cost-effective. Underpinned by our 24x7x365 Security Operations Centre (SOC), our experts ensure you have access to cybersecurity expertise when you need it the most.